Drizzle with Amazon RDS and SST
You can use SST to deploy an Amazon Postgres RDS database and set up Drizzle ORM and Drizzle Kit to manage it.
Before you get started, make sure to configure your AWS credentials.
Examples
We also have a few other Drizzle and Postgres examples that you can refer to.
- Run migrations in your CI/CD pipeline
- Run Postgres in a local Docker container for dev
- Use Next.js, Postgres, and Drizzle with the T3 Stack
1. Create a project
Let’s start by creating a Node.js app.
mkdir aws-drizzle && cd aws-drizzlenpm init -yInit SST
Now let’s initialize SST in our app.
npx sst@latest initnpm installSelect the defaults and pick AWS. This’ll create a sst.config.ts file in your project root.
Init Drizzle
Add Drizzle to your project. We’re also adding the pg client that Drizzle will use.
npm install pg @types/pg drizzle-orm drizzle-kitDrizzle ORM is what will be used to query our database, while Drizzle Kit will allow us to run migrations. It also comes with Drizzle Studio, a query browser.
Let’s add the following to the scripts in the package.json.
"scripts": { "db": "sst shell drizzle-kit"},The sst shell CLI will pass the credentials to Drizzle Kit and allow it to connect to your database.
Let’s also update our tsconfig.json.
{ "compilerOptions": { "strict": true }}2. Add a Postgres db
Let’s add a Postgres database using Amazon RDS. This needs a VPC. Update your sst.config.ts.
async run() { const vpc = new sst.aws.Vpc("MyVpc", { bastion: true, nat: "ec2" }); const rds = new sst.aws.Postgres("MyPostgres", { vpc, proxy: true });},The proxy option configures an RDS Proxy behind the scenes making it ideal for serverless applications.
While the bastion option will let us connect to the VPC from our local machine. We also need the NAT gateway for this example since we’ll be using a Lambda function, and this allows a Lambda function that’s in a VPC to access the internet.
Start Drizzle Studio
When you run SST in dev it can start other dev processes for you. In this case we want to start Drizzle Studio. Add this below the Postgres component.
new sst.x.DevCommand("Studio", { link: [rds], dev: { command: "npx drizzle-kit studio", },});This will run the given command in dev.
Add an API
We’ll use a Lambda function as an API to query our database. Add the following to your sst.config.ts below the database config.
new sst.aws.Function("MyApi", { vpc, url: true, link: [rds], handler: "src/api.handler",});We are linking our database to the API.
Install a tunnel
Since our database cluster is in a VPC, we’ll need a tunnel to connect to it from our local machine.
sudo npx sst tunnel installThis needs sudo to create a network interface on your machine. You’ll only need to do this once on your machine.
Start dev mode
Start your app in dev mode. This runs your functions Live.
npx sst devIt’ll take a few minutes to create your database. Once complete, you’ll see this.
✓ Complete MyApi: https://ouu5vovpxllyn5b6ot2nn6vdsa0hvcuj.lambda-url.us-east-1.on.awsYou’ll see Drizzle Studio started in a tab called Studio. And a tunnel in the Tunnel tab.
3. Create a schema
Let’s define our Drizzle config. Add a drizzle.config.ts in your project root with this.
import { Resource } from "sst";import { defineConfig } from "drizzle-kit";
export default defineConfig({ dialect: "postgresql", // Pick up all our schema files schema: ["./src/**/*.sql.ts"], out: "./migrations", dbCredentials: { host: Resource.MyPostgres.host, port: Resource.MyPostgres.port, user: Resource.MyPostgres.username, password: Resource.MyPostgres.password, database: Resource.MyPostgres.database, },});Here we are telling Drizzle that we’ll be specifying your database schema in .sql.ts files in our src/ directory.
We are going to create a simple database to store some todos. Create a new file in src/todo.sql.ts with the following.
import { text, serial, pgTable } from "drizzle-orm/pg-core";
export const todo = pgTable("todo", { id: serial("id").primaryKey(), title: text("title").notNull(), description: text("description"),});4. Generate a migration
We can use this to generate a migration.
npm run db generateThis in turn runs sst shell drizzle-kit generate and creates a new migration in the migrations/ directory.
Apply the migration
Now we can apply our migration using.
npm run db migrateThis should create our new schema.
This needs the tunnel to connect to the database. So you should have sst dev in a separate terminal.
npx sst tunnelAlternatively, you can just run the tunnel using the above command.
Drizzle Studio
To see our schema in action we can open the Drizzle Studio. Head over to the Studio tab in your sst dev session and go to the link.
Or head over to https://local.drizzle.studio in your browser.
5. Query the database
To use Drizzle ORM to query our database, create a new src/drizzle.ts config file with the following.
import { drizzle } from "drizzle-orm/node-postgres";import { Pool } from "pg";import { Resource } from "sst";import * as schema from "./todo.sql";
const pool = new Pool({ host: Resource.MyPostgres.host, port: Resource.MyPostgres.port, user: Resource.MyPostgres.username, password: Resource.MyPostgres.password, database: Resource.MyPostgres.database,});
export const db = drizzle(pool, { schema });Now we can use that in the API. Create our API handler in src/api.ts.
import { db } from "./drizzle";import { todo } from "./todo.sql";import { APIGatewayProxyEventV2 } from "aws-lambda";
export const handler = async (evt: APIGatewayProxyEventV2) => { if (evt.requestContext.http.method === "GET") { const result = await db.select().from(todo).execute();
return { statusCode: 200, body: JSON.stringify(result, null, 2), }; }
if (evt.requestContext.http.method === "POST") { const result = await db .insert(todo) .values({ title: "Todo", description: crypto.randomUUID() }) .returning() .execute();
return { statusCode: 200, body: JSON.stringify(result), }; }};For POST requests we create a new todo and for GET requests we simply print out all our todos.
Test your app
To test our app, make a POST request to our API.
curl -X POST https://ouu5vovpxllyn5b6ot2nn6vdsa0hvcuj.lambda-url.us-east-1.on.awsNow if you head over to https://ouu5vovpxllyn5b6ot2nn6vdsa0hvcuj.lambda-url.us-east-1.on.aws in your browser, you’ll see that a todo has been added.
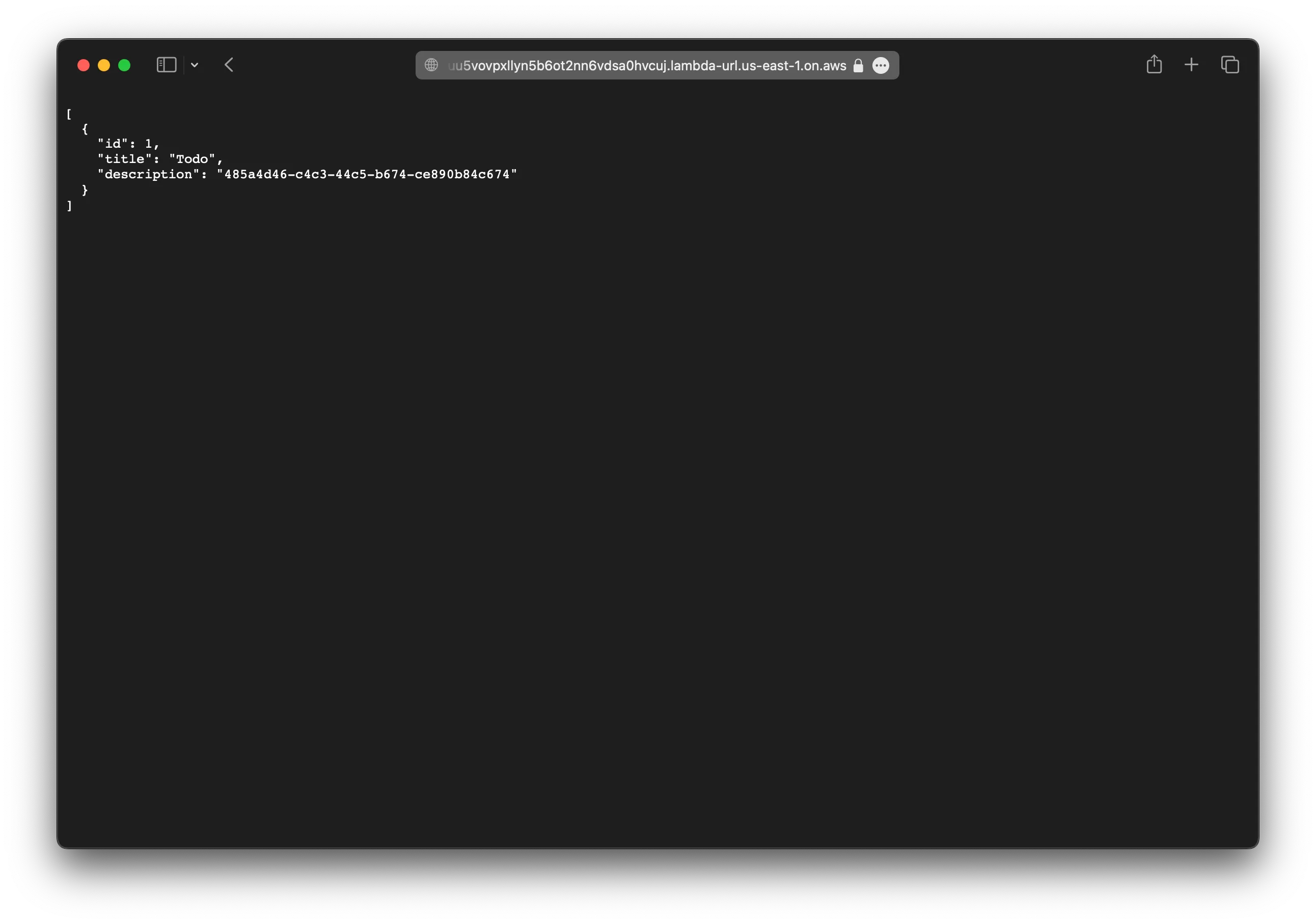
You should see this in the Drizzle Studio as well.
6. Deploy your app
Finally, let’s deploy your app.
npx sst deploy --stage productionYou can use any stage name here but it’s good to create a new stage for production.
Connect the console
As a next step, you can setup the SST Console to git push to deploy your app and monitor it for any issues.
You can create a free account and connect it to your AWS account.